
The ports used for data (clientserver) are negotiated through this channel. Secure command channel: requested by AUTH TLS (explicit) or AUTH SSL (implicit) commands. Separate generic SSL session for data transfer using dynamic ports. 'Explicit FTP Proxy' does not work for FTPS prior to FortiOS 6.2.1 (for the same internal ID as above).ġ) FTPs-implicit (outdated) -the entire FTPS session is encrypted uses:
#Filezilla ftp slow folder travseral how to
FortiGate can't differentiate based on the embedded signature of the sFTP from SSH.Ī custom signature is needed to block SSH but allow SFTP ( Technical Tip: How to block SSH but allow SFTP using the same TCP port 22).įTPs - FTP+Authentication (FTP over TLS or SSL extension of FTP protocol: uses :įortiOS support for FTPs is introduced starting with FortiOS 6.4 (and not supported in versions older than 6.4, for Mantis 532698). SFTP is not supported/detected by the FTP signature (564518). SFTP - Secure FTP (or 'FTP over SSH' extension of SSH protocol): uses SSH port 22 Nowadays SFTP should read 'sFTP' and refers to 'Secure FTP'. Protocol not used anymore (assigned Historic status by the IETF = not used anymore). SFTP - Simple FTP (RFC913): uses port 115. TFTP - Trivial File Transfer Protocol ( RFC 1350): uses UDP 69 tftp session-helper operates as above. FortiGate opens the session expectation accordingly). (FTP helper in FortiGate checks the port because the FTP command port is not encrypted.
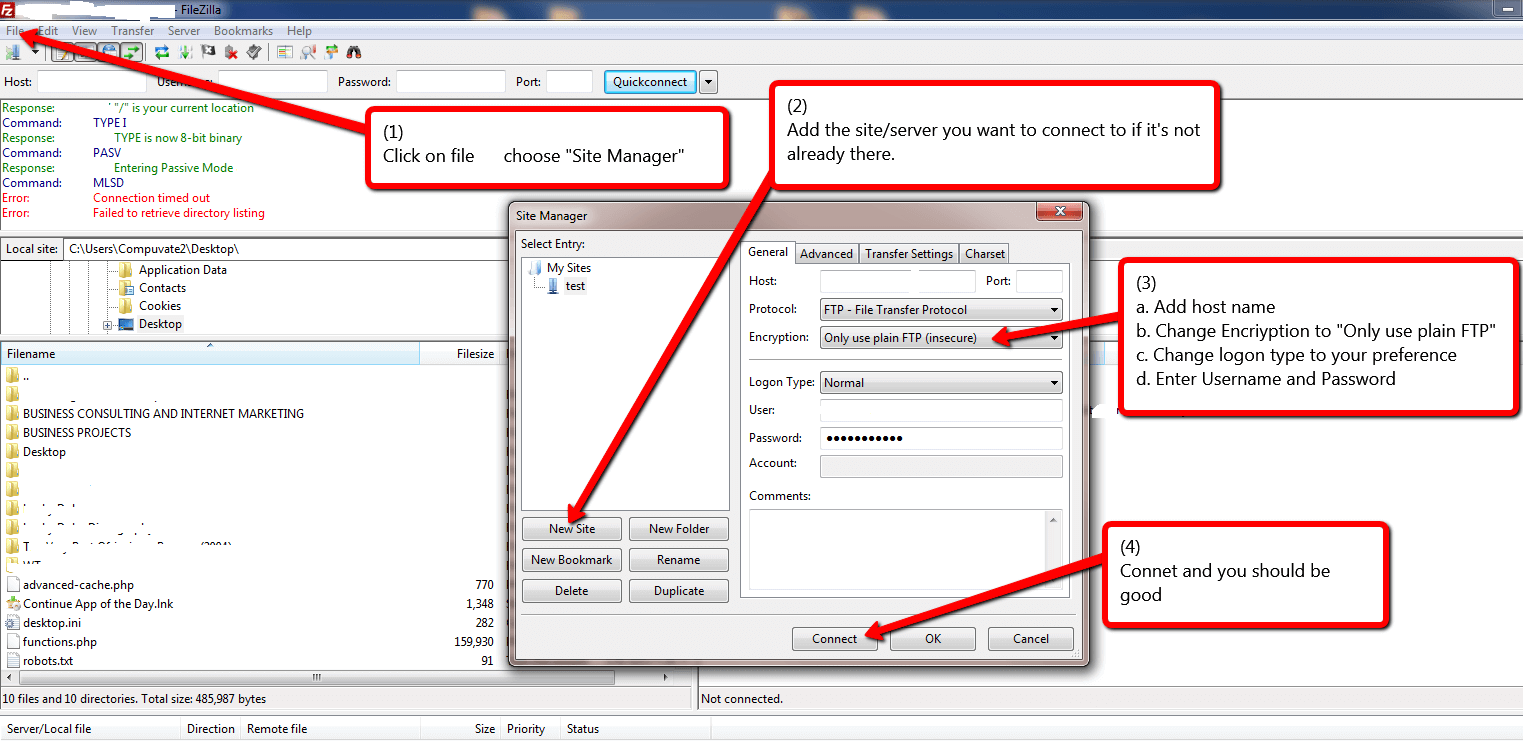
Passive: client tells the server which port to use for data. (default mode uses port20 not suitable if Firewall does not explicitly opens this port). Active: server tells the client the port to use for data. Technical terms are explained in relation to what firewall ports need to be open to allow the traffic.įTP - File Transfer Protocol: uses TCP port 21 for command and TCP port 20 for data transfer. It contains the basic mode of operation, differences, and explanations. This article describes the FTP suite of protocols (FTPs, sFTP, SFTP).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
